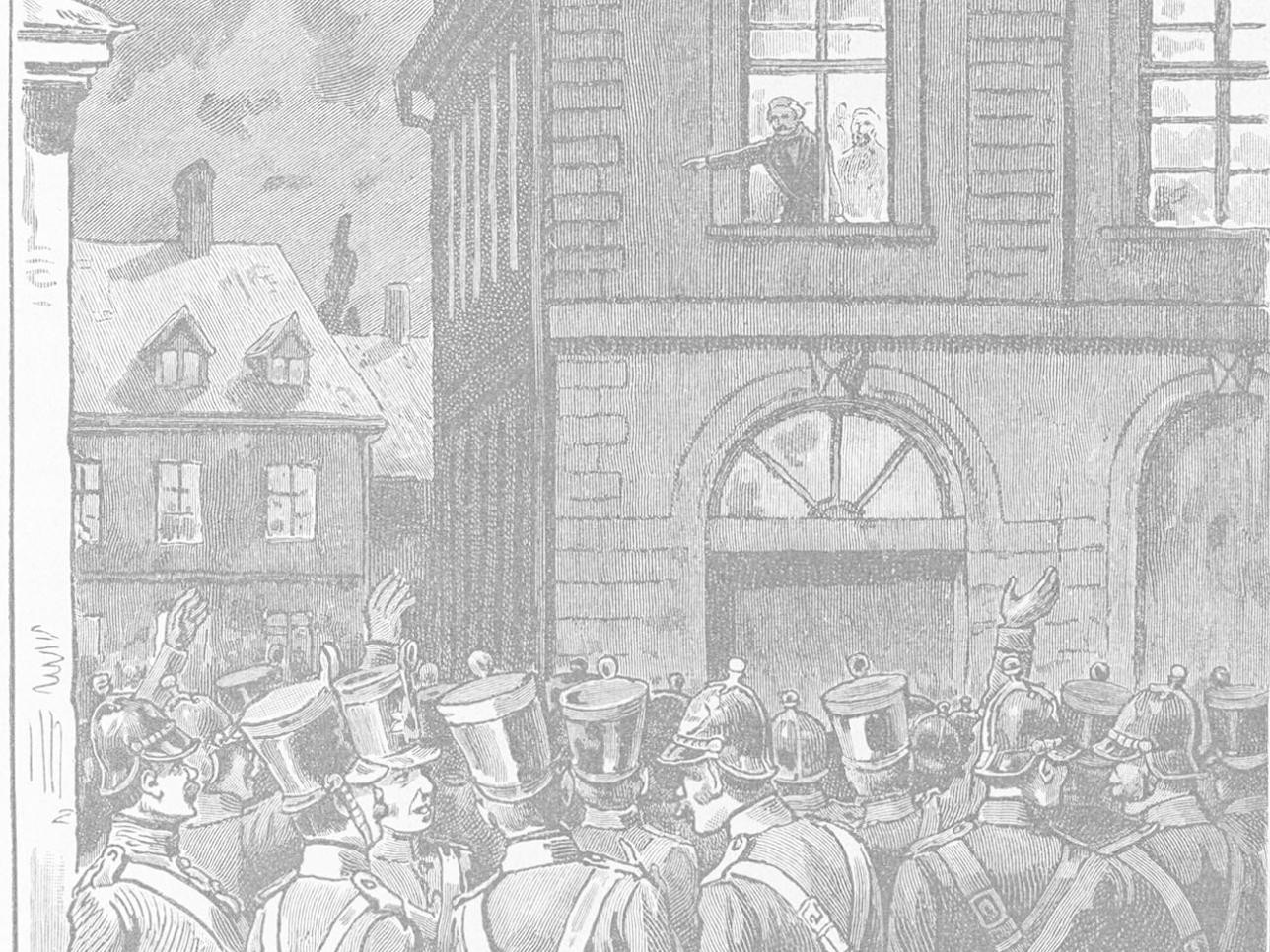City history at a glance
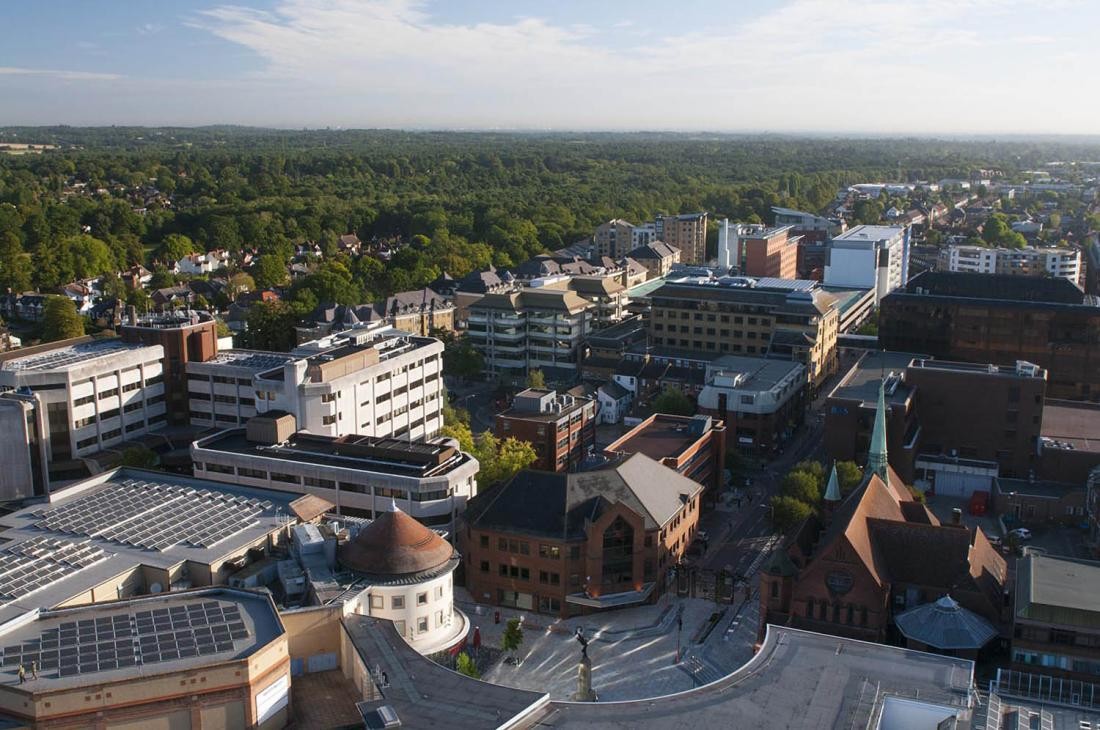
Many important historical events, such as the Peace of Rastatt and the Baden Revolution, have shaped Rastatt over the past centuries. Two castles dating back to the reign of the Margraves of Baden-Baden remain landmarks of the town to this day. Since 1956, Rastatt has been a large district town, the largest town in the district of Rastatt and an important business location between Karlsruhe and Offenburg. Over 50,000 citizens from 127 countries now live in the baroque town.
1084
The first documented mention of Rastatt can be found under the name "Rastetten" in a manuscript from Hirsau Abbey dating back to 1084.
1203
the first mention of a church in Rastatt dates back to 1203. This is today's Bernharduskirche.
1404
King Ruprecht of the Palatinate granted the town market rights in 1404. The market develops into a preferred trading center for Alsatian wine. This is why Rastatt still has the wine ladder in its coat of arms today.
1700
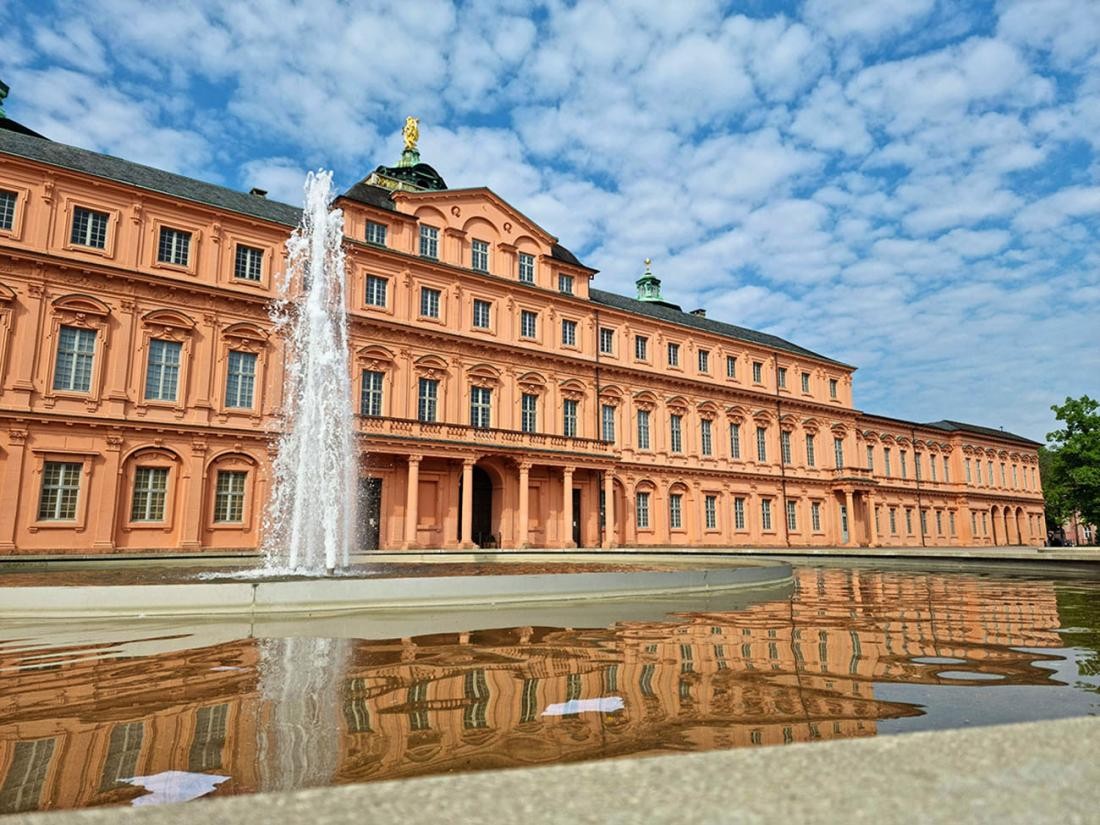
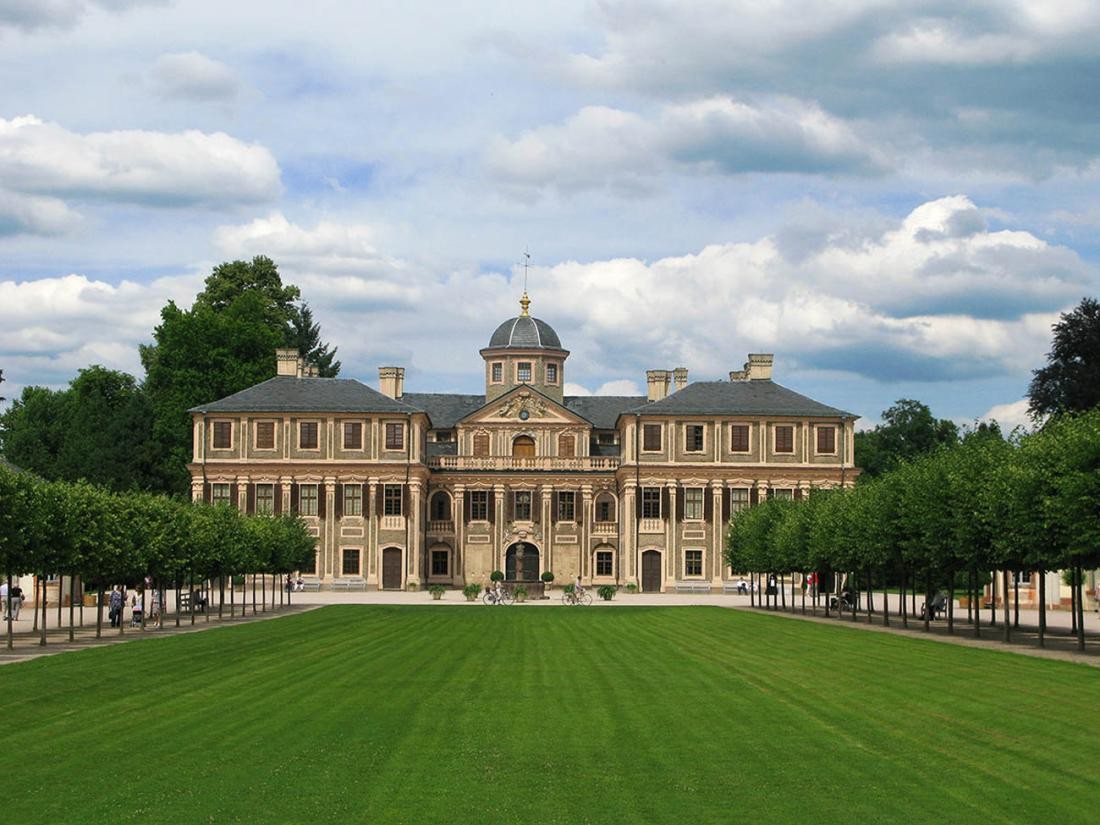
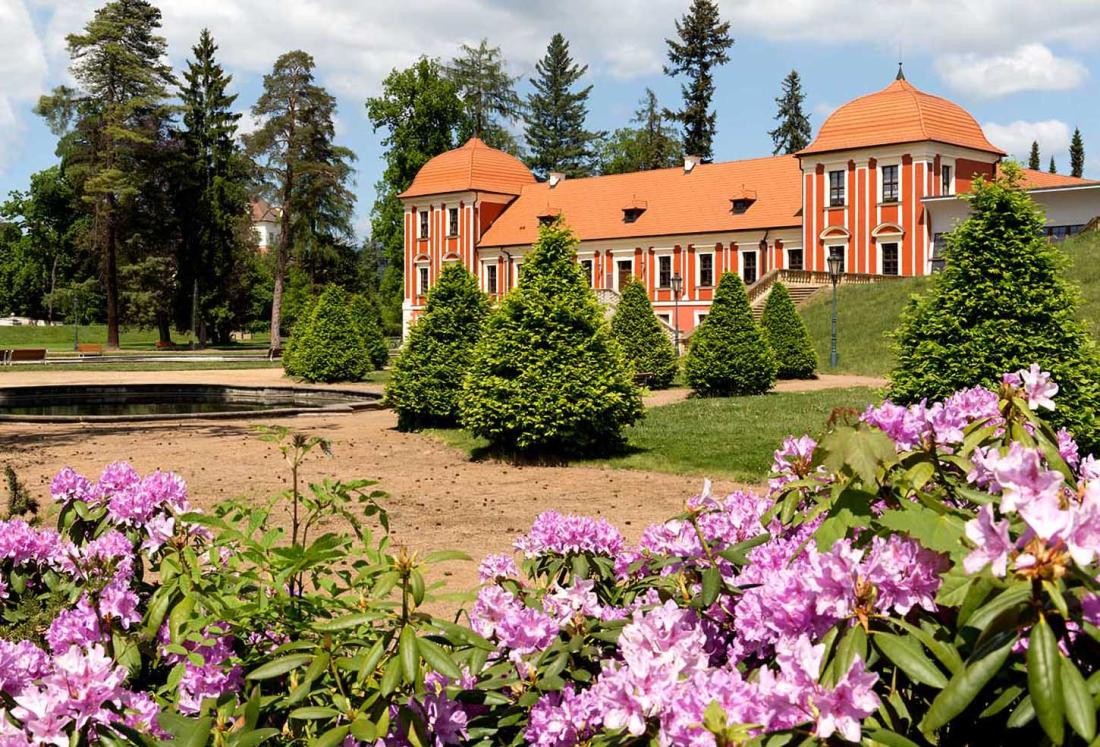
Margrave Ludwig Wilhelm von Baden-Baden, who ruled from 1677 to 1707, decided in 1700 to expand his initially planned hunting lodge into a modern Baroque residence: Today's Rastatt Palace is built. Around 1700, Rastatt was granted city rights.
1705
The Rastatt Residential Palace is one of the earliest German examples of an imitation of the Palace of Versailles. In 1705, Margrave Ludwig Wilhelm von Baden-Baden and his family moved into the side wing of the palace. Ludwig Wilhelm died just two years later in January 1707 and from then on, his wife Sibylla Augusta ruled the country as regent for 20 years.
1714
in 1714, Rastatt is the scene where European history is written. The Peace of Rastatt marks the end of the War of the Spanish Succession, in which all the major European powers have been involved since 1701. Rastatt Palace is the venue for the four-month peace negotiations.
1771
When the Baden-Baden line died out in 1771, the margraviate fell to the Protestant Baden-Durlach.
1797 to 1799
The new state government under Margrave Karl Friedrich takes various initiatives to promote Rastatt's economy. These included the organization of the Rastatt Congress, which met in the palace from 1797 to 1799, and the founding of a wagon factory.
The court court and later the Middle Rhine district government were also established in Rastatt. In the first half of the 19th century, the town of Rastatt developed into a prosperous administrative center.
1811
Rastatt becomes the capital of the Murg district and garrison of the German Confederation.
1842
Construction of the Rastatt Federal Fortress begins in 1842. For the town of Rastatt, this represents a major turning point in the town's development. The townscape and life in the town changed fundamentally. The authorities move away and economic development is now very limited and heavily dependent on the military.
1844
The Karlsruhe-Rastatt railroad line is opened on May 1, 1844. The Rastatt-Oos section follows on May 6.
1849
in 1849, Rastatt is the central scene of the Baden Revolution. From July 1 to 23, a large part of the revolutionary troops (5,500 men) withdraw into the federal fortress, while the Prussians besiege the fortress outside. On July 23, the revolutionaries capitulate to the Prussian besiegers.
1890
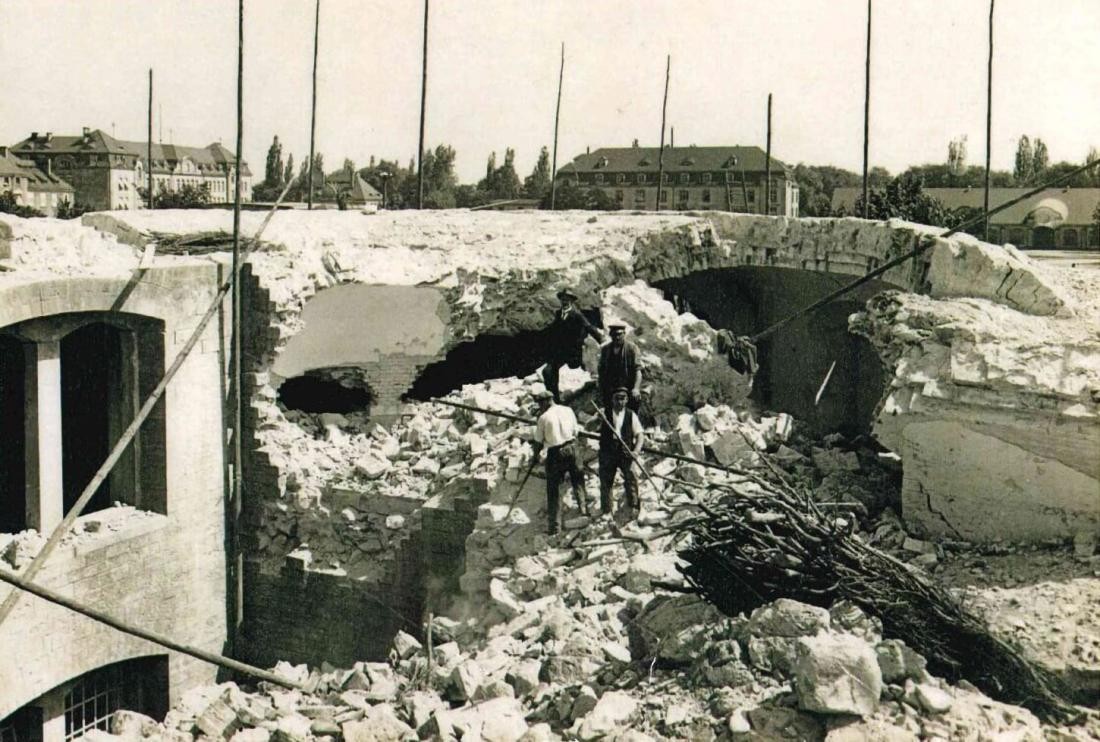
in 1890, the fortress was abandoned and then largely demolished. With the demolition of the fortress, Rastatt becomes an open city again. New industrial companies come to Rastatt and bring prosperity to the town.
The First and Second World Wars
The First World War and the Great Depression put a stop to the economic upturn in Rastatt. Everyday life in the coming decades is characterized by unemployment, housing shortages and poverty. During the Third Reich, Rastatt once again becomes a garrison town and narrowly escapes destruction in the Second World War.
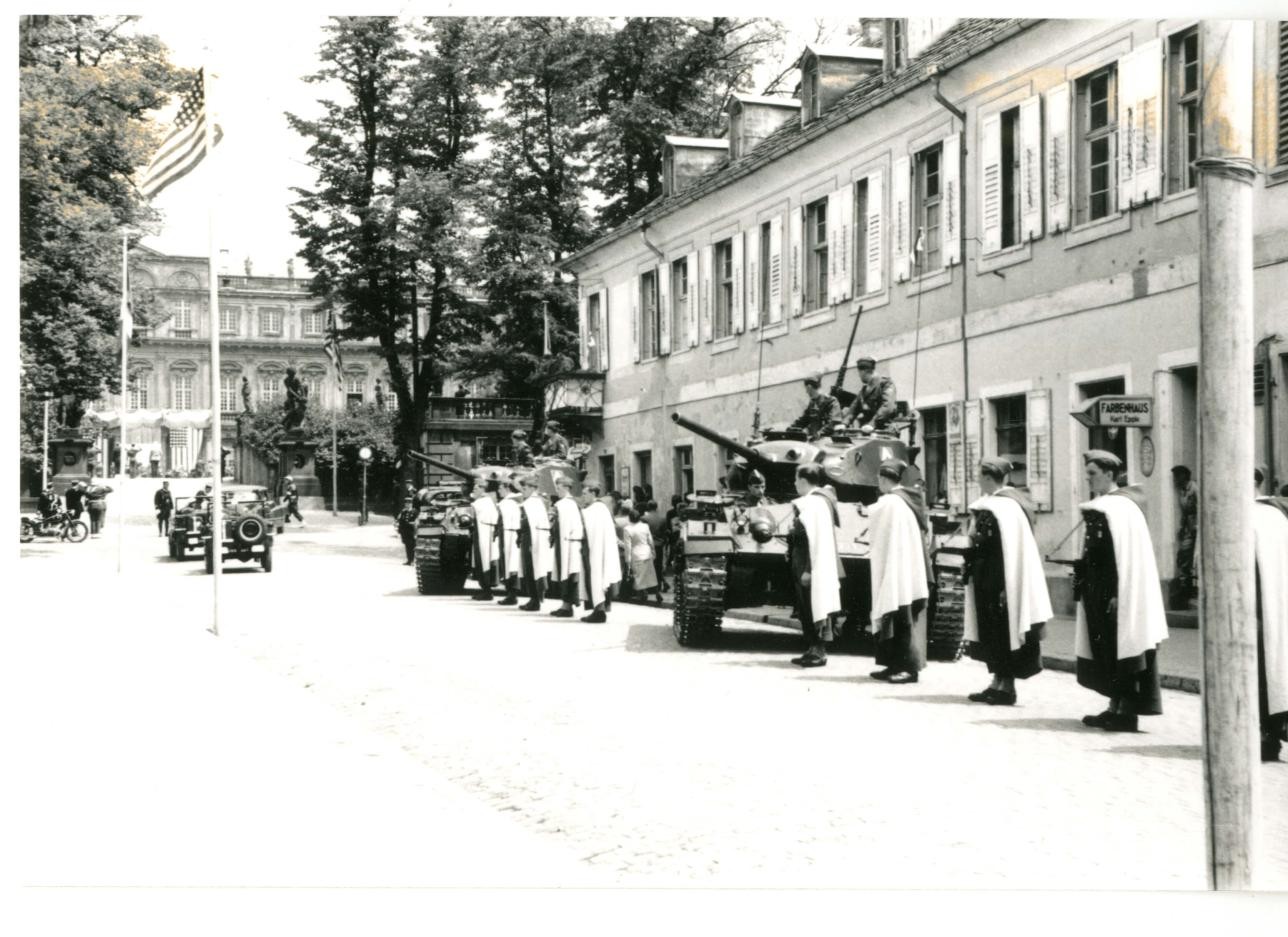
After the war, French soldiers moved into the barracks and shaped life in the town until their departure in the 1990s.
1946
On September 15, for the first time after more than 12 years of dictatorship, the population elects a city council consisting of 12 men according to democratic principles.
1946-1954
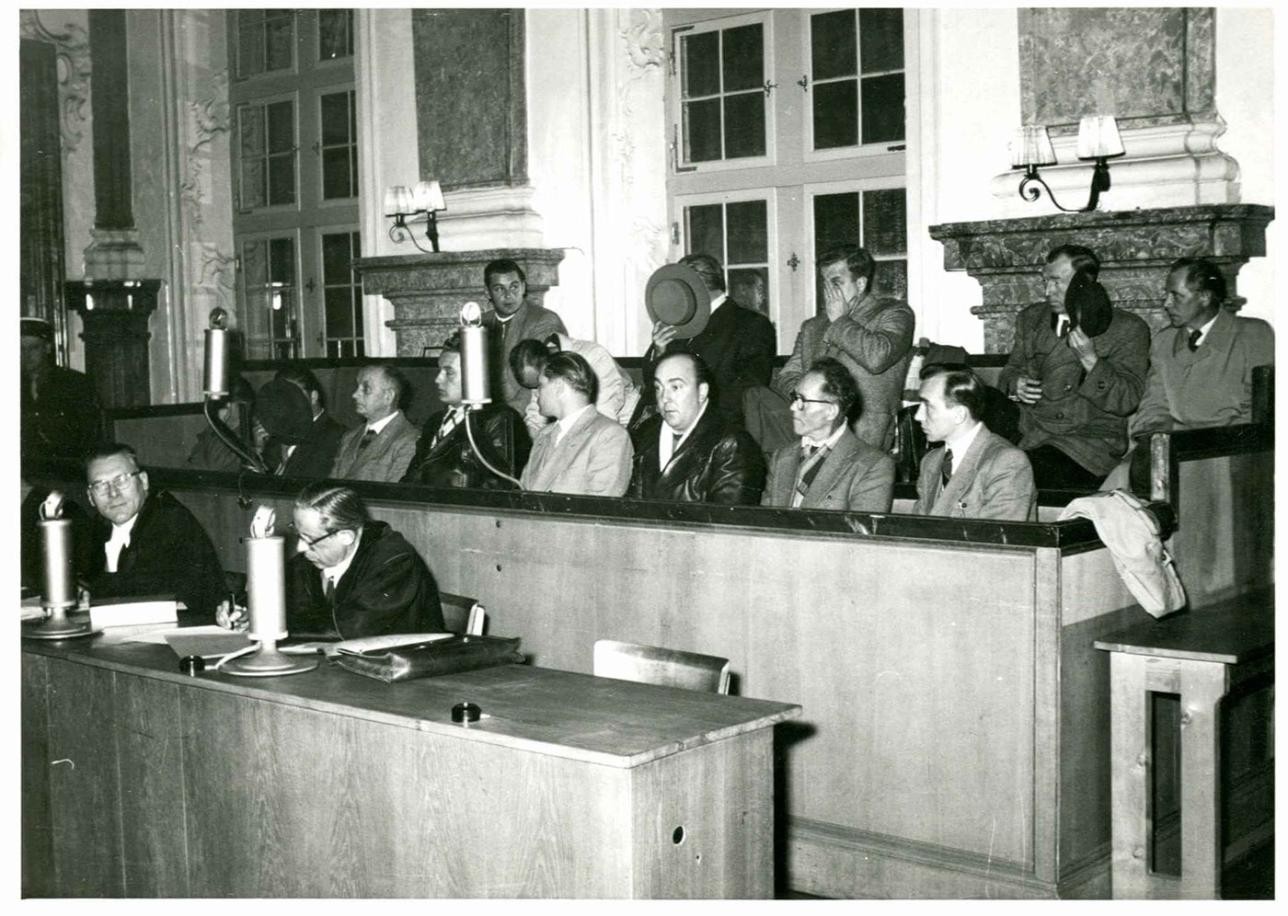
The so-called "Rastatt Trials " against those responsible for the German Reich during the National Socialist era take place at Rastatt Castle before the French Tribunal général. By 1949, 235 trials against National Socialist officials were held; appeals were heard before the Tribunal supérieur until 1954.
1956
Rastatt has been a large district town since April 1, 1956.
1965
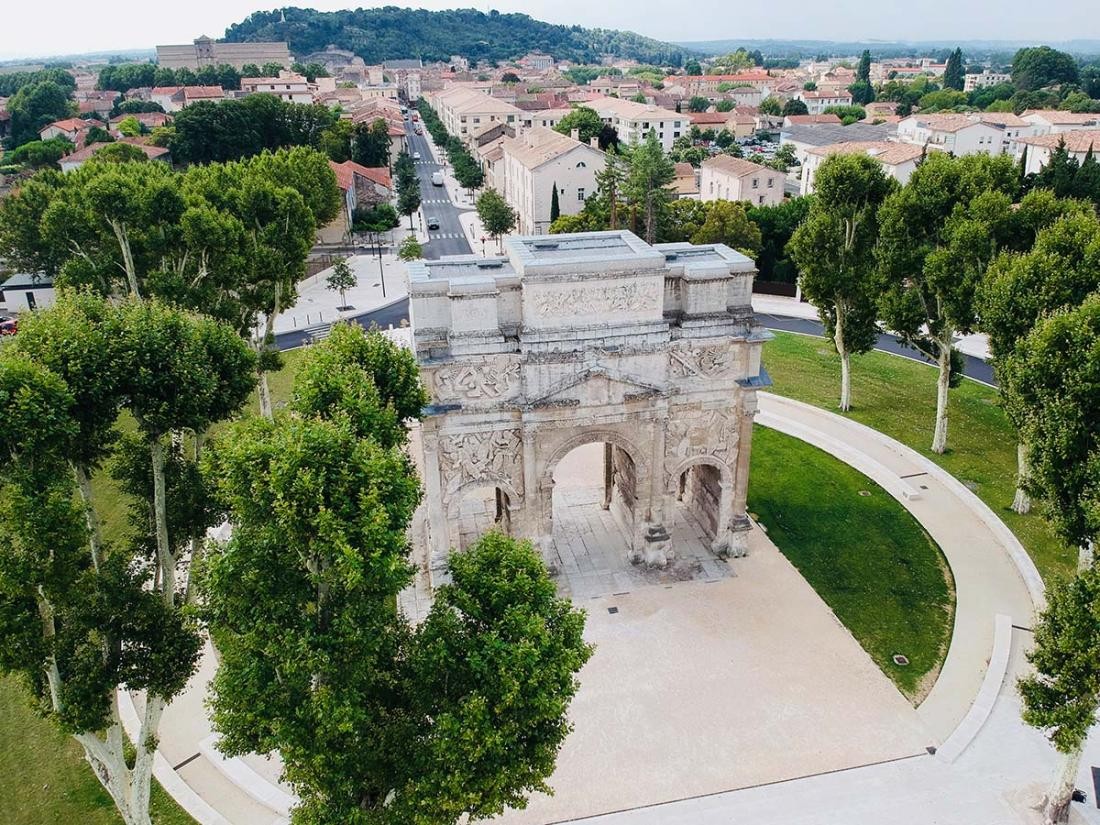
The town has been twinned with Orange in Provence, France, since 1965.
1971-1974
In the course of the municipal reform in the 1970s, Niederbühl, Plittersdorf, Ottersdorf, Wintersdorf and Rauental are incorporated.
1984
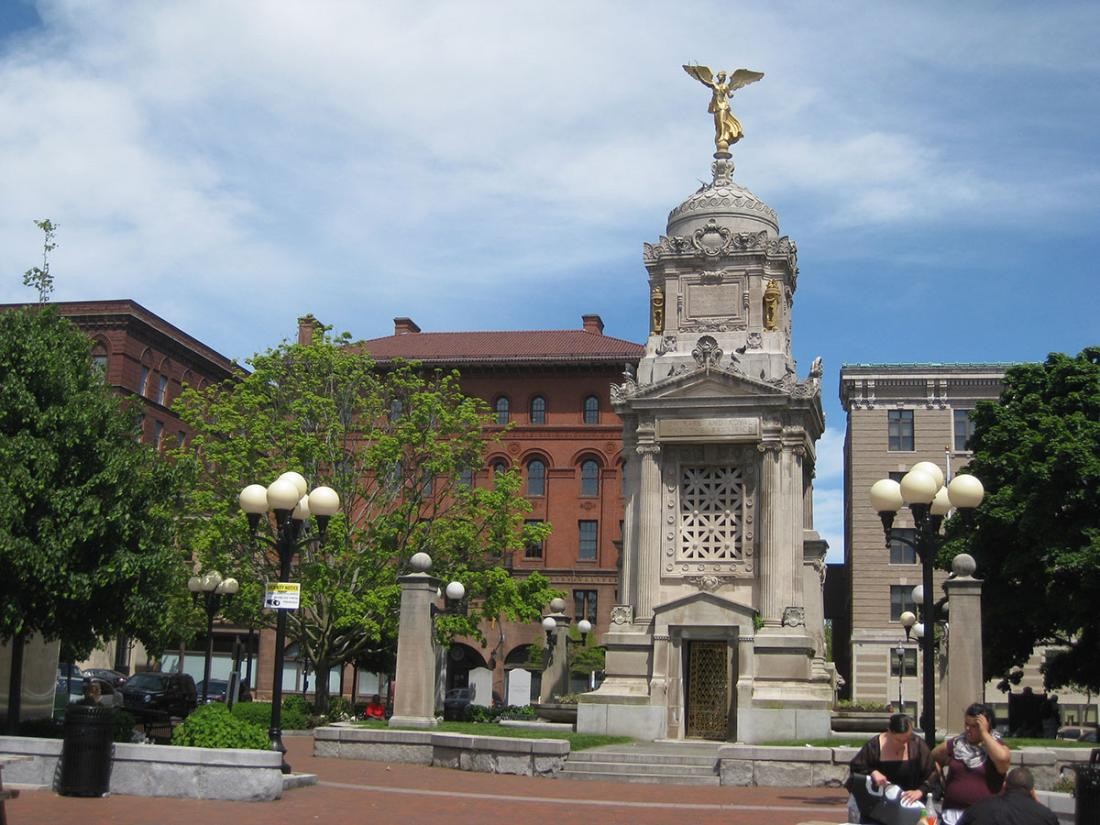
Rastatt is twinned with New Britain in the USA in 1984.
1986
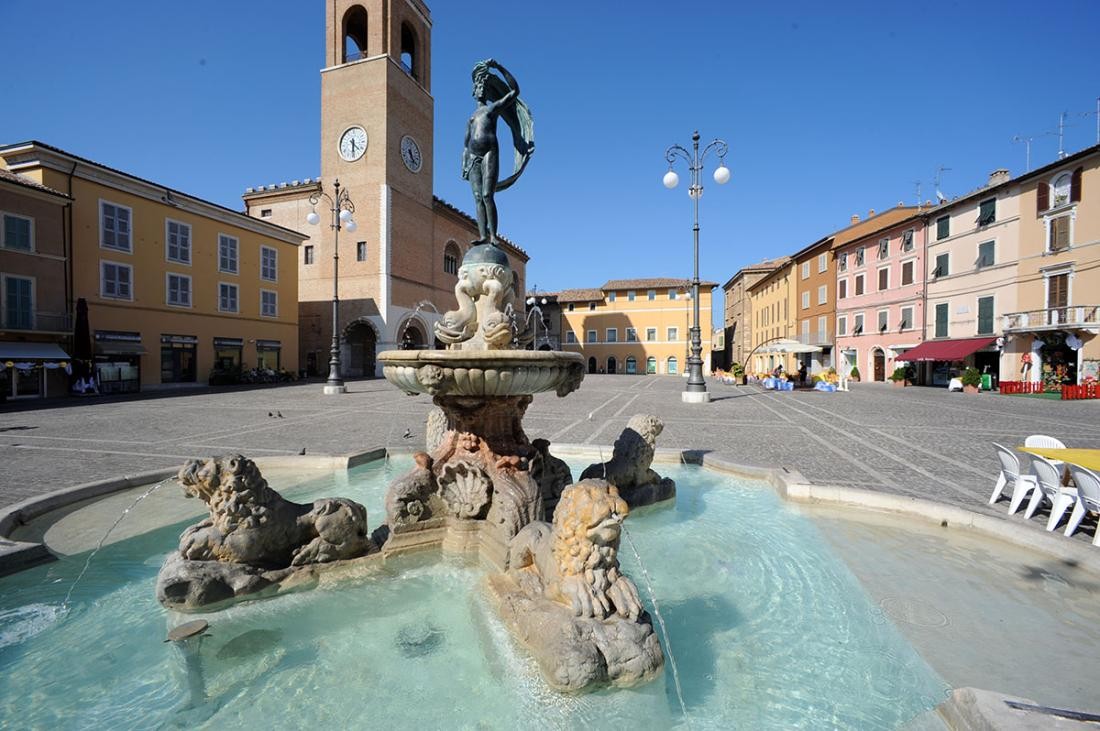
Two years later, in 1986, the town twinning between Rastatt and Fano in Italy is signed.
1988
The city of Rastatt's relations extend as far as Brazil. There has been a sponsorship with Entre Rios in Brazil since 1988.
1991
in 1991, Rastatt enters into its fourth town twinning with the Czech town of Ostrov (formerly Schlackenwerth).
1993
As a farewell gift to the departing French soldiers, the international street theater festival "tête-à-tête" is held in Rastatt for the first time in 1993. It remains a highlight in the city's cultural calendar to this day.
1997
With the opening of a Daimler AG plant in 1997, Rastatt becomes an important location for the automotive industry.
2001
in 2001, the town of Rastatt expands its connections abroad. Woking in England is now the fifth twin town.

%202015.jpg?f=%2Fsite%2FRastatt-Stadt%2Fget%2Fparams_E914290577%2F3348234%2FHeaderbild_Goldener%2520Mann%2520Luftbild%2520%2528Joachim%2520Gerstner%2529%25202015.jpg&w=2500&h=648&m=C)